Department Seminars & Colloquia
When you're logged in, you can subscribe seminars via e-mail
A graph G on n vertices is pancyclic if it contains cycles of length t for all 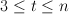 . We prove that for any fixed
. We prove that for any fixed 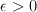 , the random graph G(n,p) with
, the random graph G(n,p) with 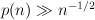 asymptotically almost surely has the following resilience property. If H is a subgraph of G with maximum degree at most
asymptotically almost surely has the following resilience property. If H is a subgraph of G with maximum degree at most 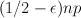 then G-H is pancyclic. In fact, we prove a more general result which says that if
then G-H is pancyclic. In fact, we prove a more general result which says that if 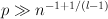 for some integer
for some integer 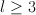 then for any
then for any 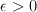 , asymptotically almost surely every subgraph of G(n,p) with minimum degree greater than
, asymptotically almost surely every subgraph of G(n,p) with minimum degree greater than 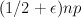 contains cycles of length t for all
contains cycles of length t for all 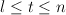 . These results are tight in two ways. First, the condition on p essentially cannot be relaxed. Second, it is impossible to improve the constant 1/2 in the assumption for the minimum degree.
. These results are tight in two ways. First, the condition on p essentially cannot be relaxed. Second, it is impossible to improve the constant 1/2 in the assumption for the minimum degree.
Joint work with Michael Krivelevich and Benny Sudakov.
The popular neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm used in phylogenetics is a greedy algorithm for finding the balanced minimum evolution (BME) tree associated to a dissimilarity map. From this point of view, NJ is "optimal'' when the algorithm outputs the tree which minimizes the balanced minimum evolution criterion. We use the fact that the NJ tree topology and the BME tree topology are determined by polyhedral subdivisions of the spaces of dissimilarity maps ${∖R}_{+}^{n choose 2}$ to study the optimality of the neighbor-joining algorithm. In particular, we investigate and compare the polyhedral subdivisions for . A key requirement is the measurement of volumes of spherical polytopes in high dimension, which we obtain using a combination of Monte Carlo methods and polyhedral algorithms. We show that highly unrelated trees can be co-optimal in BME reconstruction, and that NJ regions are not convex. We obtain the radius for neighbor-joining for and we conjecture that the ability of the neighbor-joining algorithm to recover the BME tree depends on the diameter of the BME tree. This is joint work with K. Eickmeyer, P. Huggins, and L. Pachter.
In this talk we study the computation of Markov bases for contingency tables whose cell entries have an upper bound. In general a Markov basis for unbounded contingency table under a certain model differs from a Markov basis for bounded tables. Rapallo, (2007) applied Lawrence lifting to compute a Markov basis for contingency tables whose cell entries are bounded. However, in the process, one has to compute the universal Gröbner basis of the ideal associated with the design matrix for a model which is, in general, larger than any reduced Gröbner basis. Thus, this is also infeasible in small- and medium-sized problems. Here we focus on bounded two-way contingency tables under independence model and show that if these bounds on cells are positive, i.e., they are not structural zeros, the set of basic moves of all minors connects all tables with given margins. We end this talk with an open problem that if we know the given margins are positive, we want to find the necessary and sufficient condition on the set of structural zeros so that the set of basic moves of all minors connects all incomplete contingency tables with given margins. This is joint work with F. Rapallo.
The popular neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm used in phylogenetics is a greedy algorithm for finding the balanced minimum evolution (BME) tree associated to a dissimilarity map. From this point of view, NJ is "optimal'' when the algorithm outputs the tree which minimizes the balanced minimum evolution criterion. We use the fact that the NJ tree topology and the BME tree topology are determined by polyhedral subdivisions of the spaces of dissimilarity maps ${∖R}_{+}^{n choose 2}$ to study the optimality of the neighbor-joining algorithm. In particular, we investigate and compare the polyhedral subdivisions for . A key requirement is the measurement of volumes of spherical polytopes in high dimension, which we obtain using a combination of Monte Carlo methods and polyhedral algorithms. We show that highly unrelated trees can be co-optimal in BME reconstruction, and that NJ regions are not convex. We obtain the radius for neighbor-joining for and we conjecture that the ability of the neighbor-joining algorithm to recover the BME tree depends on the diameter of the BME tree. This is joint work with K. Eickmeyer, P. Huggins, and L. Pachter.
The mysterious relationship between modular forms (or more generally automorphic representations) and Galois representations has become one of the most interesting and fruitful research topic since more than 50 years ago. I will review some of the past success and report on some of the recent development.
This begins with an introduction to the subject. Graduate students are particularly welcomed.
| We shall introduce a definition for Hochschild homology of a separated presheaf/sheaf of abelian groups on a small Grothendieck site C = (C, \tau ). The starting point is the well known one to one correspondence between presheaves on a category C and categories fibred in sets over C (due to SGA1). The method can also be extended to define Hochschild homology for a separated presheaf/sheaf of sets. |
Our main objective is to extend the motivic filtration of Shuji Saito to bivariant Chow groups. We start by defining a cycle class map from the bivariant chow groups to the bivariant cohomology groups. The cycle class map enables us to define a filtration on the bivariant chow groups; in fact, we will have two possible definitions for this filtration, which we shall show later to be equivalent.
Let K be a geometric Galois extension of the rational function field k=F_q (t ). Let O_k be the integral closure of k=F_q [t ] in K. Let U_k be the group of units of Ok and Uv be the group of local units of K_v . In this note, we will consider the following problem: whether there exists a finite place P of F_q (t ) such that the natural map U_K /U_K^d → ∏_v/P U_v / U_v is injective, where d>1 is a factor of q-1.
We present a new mathematical model for a multi-name credit employing a stochastic flocking. Flocking mechanisms have been used in a variety of modeling of biological, sociological and physical aggregation phenomena. As a direct application of flocking mechanisms, we introduce a credit risk model based on community flocking for a credit worthiness index(CWI). Correlations between different credit worthiness indices are explained in terms of interaction rate as in the flocking system. Based on the flocking model for CWI, we provide a credit curve for individual names and default time distribution. We study how to price credit derivatives such as a credit default swap(CDS) and a collateralized debt obligation(CDO) with the proposed model.
Algebraic statistics is a maturing discipline whose main focus is the study of statistical inference using tools from algebraic geometry and computational algebra. Its underlying idea is that statistical models can be viewed as algebraic varieties. We discuss some of the basics in this field, with emphasis on topics covered in the speaker's recent book with Mathias Drton and Seth Sullivant, titled "Lectures on Algebraic Statistics".
Convex algebraic geometry is concerned with emerging interactions between convex optimization and algebraic geometry. A primary focus lies on the geometric underpinnings of semidefinite programming. This lecture offers a self-contained introduction. Starting with elementary questions concerning multi focal ellipses in the plane, we move on to discuss singularities and projections of spectrahedra, and new algorithms for real algebraic varieties.
We study Linear Independence (LI) assumption (sometimes called Grand Simplicity Hypothesis), which
says that the ordinates of nontrivial zeros of zeta/L-functions do not satisfy any linear relation
over rationals. LI has been used to study certain problems in analytic number theory, including the
work of Rubinstein and Sarnak on prime number races and Ng on the growth rate of the summatory
function of the Moebius function. We review the work of Rubinstein and Sarnak and that of Ng and
consider the counterparts of their results in the function field setting.
Behavioral Finance의 주요 이슈인 Prospect Theory, Mental Accounting, Overconfidence, Narrow Framing 등을 소개합니다.
금융 수학 관련 강연 안내
일시: 2009년 6월 12일(금) 오후 1시-3시
장소: 자연과학동 2411
제목: Behavioral Finance(행동 경제학=심리학+금융)
내용: Behavioral Finance의 주요 이슈인 Prospect Theory, Mental Accounting, Overconfidence, Narrow Framing 등을 소개합니다.
강사 소개
이름: 엄윤성 박사
소속: 한성대학교 경영학부
학위: 서울대학교 경영대학원 경영학과 (경영학 박사, 2007)
학력: 서울대학교 경영학과 (경영학 박사, 석사, 학사), 서울대학교 인문대학 미학과 (인문학 학사)
연구 분야: 행동주의적 재무론, 시장미시구조, 투자론
Homepage: http://www.hsba.net/prof/ys_eom/
In this talk, we introduce a surgery operation to construct surfaces in simply-connected 4-manifolds with non simply-connected complements, that are topologically equivalent but not smoothly. This construction is based on the modification of "rim surgery" introduced by Fintushel and Stern. We also construct, for any group G satisfying some simple conditions, a simply-connected symplectic manifold containing a symplectic surface whose complement has fundamental group G. In the case, we produce infinitely many smoothly inequivalent surfaces that are equivalent up to smooth s-cobordism and hence are topologically equivalent for good groups.

