학과 세미나 및 콜로퀴엄
E6-1 #1409
Discrete Math
최정옥 (Trinity College, CT)
Forbidden subposets for fractional weak discrepancy at most k
The fractional weak discrepancy of a poset (partially ordered set) P, written wd(P), is the least k such that some  satisfies f(y)-f(x)≤1 for
satisfies f(y)-f(x)≤1 for  and |f(y)-f(x)|≤k for x|y. Minimal forbidden subposets are often called obstructions. Shuchat, Shull, and Trenk determined the obstructions for the property wd(P)<1: the obstructions are 2+2 and 3+1. We determine the obstructions for the property wd(P)≤k when k is an integer. In this talk, the complete collection of the obstructions for wd(P)≤k for each k≥2 - which is an infinite set - will be discussed.
and |f(y)-f(x)|≤k for x|y. Minimal forbidden subposets are often called obstructions. Shuchat, Shull, and Trenk determined the obstructions for the property wd(P)<1: the obstructions are 2+2 and 3+1. We determine the obstructions for the property wd(P)≤k when k is an integer. In this talk, the complete collection of the obstructions for wd(P)≤k for each k≥2 - which is an infinite set - will be discussed.
This is joint work with Douglas B. West.
Given a line bundle L on a projective variety, it is natural to consider the graded section ring R(L) given by all sections of multiples of L. We call R(L) a complete section ring. Then we define a general section ring to be a subring of R(L). We will define a certain class of (not necessarily complete) section rings associated to adjoint line bundles, which contains the usual canonical rings. We will discuss its properties and why we need those rings.
Plasma is a state of matter in which electrons
disassociate from their nuclei, resulting in
electrically conducting clouds of positively
and negatively charged ions. Mathematically,
plasma can be modeled on a variety of scales,
resulting in various kinetic, fluid, and hybrid
models.
In this talk we first consider the simplest plasma fluid
model: the ideal MHD (magnetohydrodynamic) system.
We review some of the mathematical difficulties
associated with the divergence-free condition
on the magnetic field. We will then describe a
class of discontinuous Galerkin (DG) methods for
approximately solving this system.
Next we consider two genuinely two-fluid models of
plasma: Euler-Maxwell (5-moments) and extended
Euler-Maxwell (10-moments). We focus our discussion
on the problem of collisionless magnetic reconnection.
We first describe this problem and then our efforts to
apply two-fluid models to it, again using discontinuous
Galerkin methods.
Scattering refers an asymptotic behavior that a nonlinear solution converges to a linear solution as time goes to infinity. It appears in defocusing equations. I will begin with basics of dispersive equations and properties of linear solutions, and then go on nonlinear scattering problems. I will discuss this with some model equations, the nonlinear Schrodinger equation and the generalized KdV equations.
PDE 전문가 아니신 분도 참석 하시면 좋습니다.
The fifth-order KdV equation arises in the KdV hierarchy. I will discuss local well-posedness and ill-posedness of the initial value problem in the Sobolev spaces with low regularity. Unlike the KdV equation, strong low-high frequency interaction become a major obstacle for well-posedness result, but a hint for ill-posedness result. I will explain how it works in both directions.
We give an introduction to the classification of varieties of
almost minimal degree. This is done by projections of
varieties of minimal degree that are classically well-known.
In the second part of the talk we derive several
applications related to the depth conjecture, the classification
of non-normal Dell Pezzo varieties, and the classification
of non-normal hypersurfaces of degree three. We end with
problems about secant and tangent varieties of rational normal scrolls.
정보전자동 제2공동강의실 (E3-2 # 1219)
기타
T. Kailath, A. Paulraj (Stanford University)
The Magic of Mathematics in Information Technology
09:30 - 09:40 Welcome Remarks by Vice President Minho Kang
09:40 - 10:20 'Form Radiative Transfer Theory to Fast Algorithms for Cell Phones' by Prof. T.Kailath
10:20 - 10:50 Q/A Session
10:50 - 11:30 'Searching for Spectrum Efficiency' by Prof.A.Paulraj
11:30 - 12:00 Q/A Session
12:00 - 01:00 Luncheon (고급 샌드위치 제공)
A graph G on n vertices is pancyclic if it contains cycles of length t for all 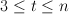 . We prove that for any fixed
. We prove that for any fixed 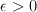 , the random graph G(n,p) with
, the random graph G(n,p) with 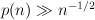 asymptotically almost surely has the following resilience property. If H is a subgraph of G with maximum degree at most
asymptotically almost surely has the following resilience property. If H is a subgraph of G with maximum degree at most 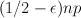 then G-H is pancyclic. In fact, we prove a more general result which says that if
then G-H is pancyclic. In fact, we prove a more general result which says that if 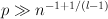 for some integer
for some integer 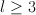 then for any
then for any 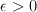 , asymptotically almost surely every subgraph of G(n,p) with minimum degree greater than
, asymptotically almost surely every subgraph of G(n,p) with minimum degree greater than 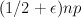 contains cycles of length t for all
contains cycles of length t for all 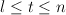 . These results are tight in two ways. First, the condition on p essentially cannot be relaxed. Second, it is impossible to improve the constant 1/2 in the assumption for the minimum degree.
. These results are tight in two ways. First, the condition on p essentially cannot be relaxed. Second, it is impossible to improve the constant 1/2 in the assumption for the minimum degree.
Joint work with Michael Krivelevich and Benny Sudakov.
The popular neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm used in phylogenetics is a greedy algorithm for finding the balanced minimum evolution (BME) tree associated to a dissimilarity map. From this point of view, NJ is "optimal'' when the algorithm outputs the tree which minimizes the balanced minimum evolution criterion. We use the fact that the NJ tree topology and the BME tree topology are determined by polyhedral subdivisions of the spaces of dissimilarity maps ${∖R}_{+}^{n choose 2}$ to study the optimality of the neighbor-joining algorithm. In particular, we investigate and compare the polyhedral subdivisions for . A key requirement is the measurement of volumes of spherical polytopes in high dimension, which we obtain using a combination of Monte Carlo methods and polyhedral algorithms. We show that highly unrelated trees can be co-optimal in BME reconstruction, and that NJ regions are not convex. We obtain the radius for neighbor-joining for and we conjecture that the ability of the neighbor-joining algorithm to recover the BME tree depends on the diameter of the BME tree. This is joint work with K. Eickmeyer, P. Huggins, and L. Pachter.
In this talk we study the computation of Markov bases for contingency tables whose cell entries have an upper bound. In general a Markov basis for unbounded contingency table under a certain model differs from a Markov basis for bounded tables. Rapallo, (2007) applied Lawrence lifting to compute a Markov basis for contingency tables whose cell entries are bounded. However, in the process, one has to compute the universal Gröbner basis of the ideal associated with the design matrix for a model which is, in general, larger than any reduced Gröbner basis. Thus, this is also infeasible in small- and medium-sized problems. Here we focus on bounded two-way contingency tables under independence model and show that if these bounds on cells are positive, i.e., they are not structural zeros, the set of basic moves of all minors connects all tables with given margins. We end this talk with an open problem that if we know the given margins are positive, we want to find the necessary and sufficient condition on the set of structural zeros so that the set of basic moves of all minors connects all incomplete contingency tables with given margins. This is joint work with F. Rapallo.
The popular neighbor-joining (NJ) algorithm used in phylogenetics is a greedy algorithm for finding the balanced minimum evolution (BME) tree associated to a dissimilarity map. From this point of view, NJ is "optimal'' when the algorithm outputs the tree which minimizes the balanced minimum evolution criterion. We use the fact that the NJ tree topology and the BME tree topology are determined by polyhedral subdivisions of the spaces of dissimilarity maps ${∖R}_{+}^{n choose 2}$ to study the optimality of the neighbor-joining algorithm. In particular, we investigate and compare the polyhedral subdivisions for . A key requirement is the measurement of volumes of spherical polytopes in high dimension, which we obtain using a combination of Monte Carlo methods and polyhedral algorithms. We show that highly unrelated trees can be co-optimal in BME reconstruction, and that NJ regions are not convex. We obtain the radius for neighbor-joining for and we conjecture that the ability of the neighbor-joining algorithm to recover the BME tree depends on the diameter of the BME tree. This is joint work with K. Eickmeyer, P. Huggins, and L. Pachter.
The mysterious relationship between modular forms (or more generally automorphic representations) and Galois representations has become one of the most interesting and fruitful research topic since more than 50 years ago. I will review some of the past success and report on some of the recent development.
This begins with an introduction to the subject. Graduate students are particularly welcomed.
| We shall introduce a definition for Hochschild homology of a separated presheaf/sheaf of abelian groups on a small Grothendieck site C = (C, \tau ). The starting point is the well known one to one correspondence between presheaves on a category C and categories fibred in sets over C (due to SGA1). The method can also be extended to define Hochschild homology for a separated presheaf/sheaf of sets. |
Our main objective is to extend the motivic filtration of Shuji Saito to bivariant Chow groups. We start by defining a cycle class map from the bivariant chow groups to the bivariant cohomology groups. The cycle class map enables us to define a filtration on the bivariant chow groups; in fact, we will have two possible definitions for this filtration, which we shall show later to be equivalent.
Let K be a geometric Galois extension of the rational function field k=F_q (t ). Let O_k be the integral closure of k=F_q [t ] in K. Let U_k be the group of units of Ok and Uv be the group of local units of K_v . In this note, we will consider the following problem: whether there exists a finite place P of F_q (t ) such that the natural map U_K /U_K^d → ∏_v/P U_v / U_v is injective, where d>1 is a factor of q-1.
We present a new mathematical model for a multi-name credit employing a stochastic flocking. Flocking mechanisms have been used in a variety of modeling of biological, sociological and physical aggregation phenomena. As a direct application of flocking mechanisms, we introduce a credit risk model based on community flocking for a credit worthiness index(CWI). Correlations between different credit worthiness indices are explained in terms of interaction rate as in the flocking system. Based on the flocking model for CWI, we provide a credit curve for individual names and default time distribution. We study how to price credit derivatives such as a credit default swap(CDS) and a collateralized debt obligation(CDO) with the proposed model.

